Passive Restraint Systems
Automatically actuated systems designed to protect the driver and passengers in a
vehicle in case of an accident. Air bags and automatic seat belts are examples of passive
restraint systems.
Pearl Paint
A type of paint system that is similar to metallic paint, but instead of minute
metal particles it uses mica -- a kind of semi transparent, crystalline mineral. The mica
absorbs and reflects light in prismatic fashion, giving dramatic, multi-dimensional
effects to the paint.
Pinion
A gear with a small number of teeth designed to mesh with a larger geared wheel
or a rack. Used in rack and pinion steering and the differential ring and pinion. (Also
see: Rack and Pinion)
Piston
A partly hollow cylindrical part closed at one end, fitted to each of the
engine's cylinders and attached to the crankshaft by a connecting rod. Each piston moves
up and down in its cylinder, transmitting the force of the combustion chamber explosion to
the crankshaft through the connecting rod.

Plenum Chamber
An enclosed area with a volume of gas in it that is under greater pressure than
the surrounding container. (Also see: Cowl Induction)
Positive Crankcase Ventilation System (PCV)
(See: Closed Crankcase Ventilation)
Power Brakes
Brakes having vacuum or hydraulic assist to multiply the driver's effort as the
brake pedal is pushed, reducing the foot pressure necessary to stop the car.
Power Steering
A steering system generally using hydraulic pressure to multiply the driver's
effort as the steering wheel is turned so that steering effort is reduced. Also called
power-assist steering.
Powertrain
The name given to the combination of engine, transmission and axle ratio for any
particular model.
QR Suspension
(See: Multi-Link Suspension)
Quartz-Halogen Headlamps
A headlamp bulb having a quartz envelope holding the tungsten filament and filled
with an inert gas containing iodine or another of the five halogen gases. The gas serves
to remove the tungsten deposits from the bulb wall and redeposit them on the filament,
preventing blackening of the bulb surface and reduction in light output. This kind of
cycle requires very high filament operation temperatures which necessitates the use of
quartz instead of glass. These lamps produce more lighting power per watt of electrical
power than standard sealed beam headlamps.
Rack and Pinion Steering
This steering system has a toothed gear known as a pinion gear on the end of the
steering shaft that mates with a rack (which is basically a geared wheel opening up and
laid flat). When the steering wheel is turned, the pinion gear turns, moving the rack to
the left or right, thus steering the wheels. Rack and pinion steering is featured on the
Sentra, Pulsar NX, Stanza, 240SX, Maxima and 300ZX. It gives a more direct, positive,
sporty feel to the steering.
Radial Ply Tires
A tire design in which the main carcass plies or cords run radially or straight out from
the bead. Often, a circumferential belt made up of low-angle (usually around 15 degrees)
plies is added to give the desired stiffness in the tread area. With this construction,
the tread area is stiff and the sidewalls are flexible, so they can act relatively
independently of each other, delivering the optimum ride characteristics.
Radiator
A device that transfers heat from the liquid coolant to the atmosphere.
Rear Window Defroster
A device which features small wires placed on the rear window. When this device
is switched on, electrical current passing through the wires causes a small amount of heat
to clear the window of frost or fog.
Recirculating Ball and Nut Steering
A steering system in which the turning forces are transmitted through ball
bearings from a worm gear on the steering shaft to a sector gear on the pitman-arm shaft.
This steering method is utilized on our Hardbody and Pathfinder models. It offers smooth,
easy control of the vehicle.

Refrigerant
The substance used in an air conditioning system. It absorbs the heat as it
changes from liquid to gas in the evaporator, then gives up the heat as it changes back to
a liquid in the condenser. Freon 12 is a common automotive refrigerant.
Resonator
A small auxiliary muffler that assists the main muffler in reducing exhaust
noise.
Rolling Resistance
This is motion-resisting force that is present from the instant the wheels begin
to turn. On normal road surfaces, rolling resistance decreases with increased tire
pressure, and it increases with vehicle weight. Rolling resistance can also be affected by
tire construction and tread design.
Scrub Radius
A feature which lessens any tendency to pull when braking during a turn. Scrub
radius is another term you may hear which is related to steering axis inclination.
Positive scrub radius is present when a line drawn through the steering axis intersects
the road surface inside of the tire centerline.
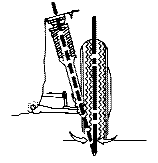
Negative scrub radius is present when a line drawn through
the;steering axis intersects the road surface outside of the tire centerline.
The effects of scrub radius are easy to visualize, using two
pieces of paper and two pencils. Lay the two rectangular pieces of paper next to each
other. These represent the tires' contact patches on the road. Now place the pencils at
the inside of the two pieces of paper, as in this first illustration. The place where the
pencil point touches the paper represents the place where the steering axis centerline
intersects the road surface. If you try to push the papers forward with the pencils, the
papers will turn outward. On a car, we would call this a tendency for the front wheels to
toe-out. (Also see: Steering Axis Inclination)
BACK
NEXT |
![]()